The Pricing Strategy In e-Commerce Is Fundamental.
Nowadays, it is straightforward to check and compare prices online. It is essential if you are selling similar products or the same products in marketplaces.
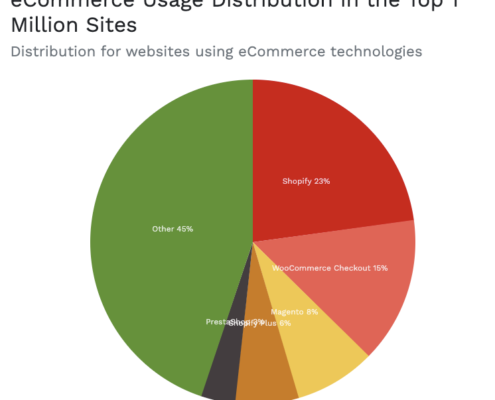
Large online retailers like Amazon, e-bay, and allegro have an advantage in competitive pricing, as they can set the price low enough to run smaller retailers out of business. But there are other ways to compete, starting with developing an eCommerce pricing strategy.
Creating a pricing strategy for a small business involves considering various elements to ensure profitability, competitiveness, and value perception. Here are the key elements to consider when developing a pricing strategy:
1. Costs and Expenses:
– Calculate all direct and indirect costs associated with producing, marketing, and selling your products or services. This includes materials, labor, overhead, marketing expenses, and any other relevant costs.
2. Profit Margin:
– Determine the desired profit margin for your products or services. This is the amount of profit you aim to generate from each sale after covering all costs.
3. Market Analysis:
– Conduct market research to understand the pricing landscape in your industry and target market. Analyze competitors’ pricing strategies, customer preferences, and willingness to pay.
4. Value Proposition:
– Define the unique value proposition of your products or services and how they differentiate from competitors. Price your offerings in alignment with the perceived value they provide to customers.
5. Customer Segmentation:
– Segment your target market based on factors such as demographics, psychographics, behavior, and purchasing power. Tailor your pricing strategy to meet the needs and preferences of different customer segments.
6. Pricing Objectives:
– Set clear pricing objectives that align with your business goals. These may include maximizing revenue, gaining market share, achieving a certain level of profitability, or positioning your brand as premium or value-oriented.
7. Pricing Models:
– Choose the most suitable pricing model for your business, such as cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, competitive pricing, or dynamic pricing. Consider factors like product lifecycle, market dynamics, and customer demand.
8. Promotions and Discounts:
– Determine when and how to offer promotions, discounts, and special offers to attract customers and drive sales. Be strategic in using discounts to avoid devaluing your products or eroding profit margins.
9. Channel Pricing:
– Consider pricing variations across different distribution channels (e.g., online store, retail partners, direct sales) to account for differences in costs, customer expectations, and competitive pressures.
10. Psychological Pricing:
– Utilize pricing psychology techniques, such as charm pricing (e.g., pricing products at $9.99 instead of $10) or prestige pricing (e.g., pricing products higher to convey exclusivity and quality), to influence customer perceptions and behavior.
11. Monitoring and Adjustments:
– Regularly monitor market conditions, competitor actions, and customer feedback to assess the effectiveness of your pricing strategy.
– Be prepared to adjust your pricing strategy as needed to adapt to changes in the market, customer preferences, or business objectives.
By carefully considering these elements, a small business can develop a pricing strategy that effectively balances profitability with customer value and competitive positioning. Regular evaluation and adjustment are essential to ensure the pricing strategy remains aligned with business goals and market dynamics over time.
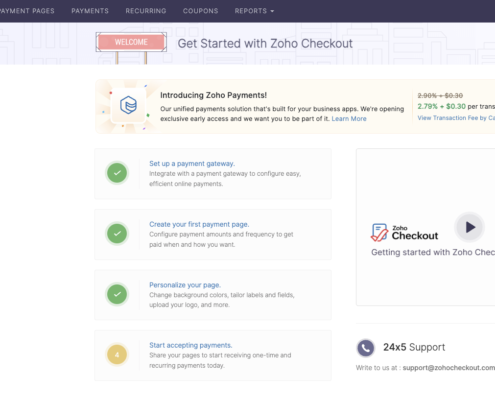
Your product offer should be exciting and diversified. You need to monitor your sales and trends in ERP, CRM and Google Analytics.
You know some seasonal ups and downs for some products and services. It is evident that in most online shops, 80% of products have to be in your offer, 10% are stars that you sell them very well, and 10% are fashion related and fast-moving.
By carefully considering these elements, a small business can develop a pricing strategy that effectively balances profitability with customer value and competitive positioning. Regular evaluation and adjustment are essential to ensure the pricing strategy remains aligned with business goals and market dynamics over time


 Digideo
Digideo Digideo
Digideo Digideo
Digideo Digideo
Digideo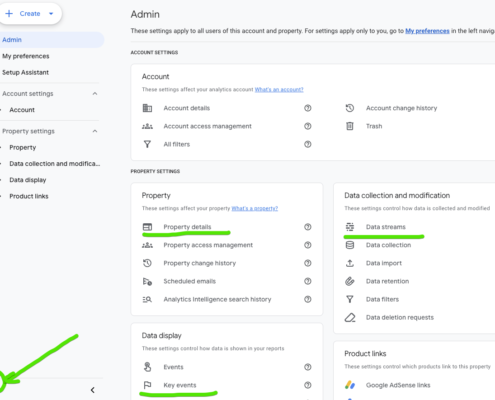


Share this entry